Decoding FAA Legal Interpretations
- Paul Simmons

- Jul 16, 2025
- 15 min read
Ever found yourself staring at a Federal Aviation Regulation (FAR), scratching your head and wondering what it actually means in your specific situation? You’re not alone. The FARs are the rulebook for the skies, but sometimes, the rules can be a bit gray, especially when new technologies like drones come into play.
This is exactly where FAA legal interpretations come in. Think of them as the official referee's call when the game's rulebook isn't perfectly clear. They provide legally binding answers that tell pilots, mechanics, and drone operators how to follow the law.
What Are FAA Legal Interpretations And Why They Matter

The FARs are massive, covering everything from how to get a pilot's license to how often an aircraft needs maintenance. But what happens when a rule is vague, or a situation pops up that the original writers never could have imagined?
That’s when the FAA’s Office of the Chief Counsel steps in. They issue these legal interpretations, which are formal, legally binding clarifications. They don't create new rules; they simply explain what an existing rule means in a real-world context. If the FARs are the U.S. Constitution for aviation, then you can think of legal interpretations as the Supreme Court rulings that apply those long-standing principles to modern life.
More Than Just Advice
It's really important to get this next part: these documents aren't just suggestions or "best practices." They carry serious legal weight.
An interpretation defines the FAA's official stance on a regulation. While not a regulation itself, courts typically give great deference to an agency's interpretation of its own rules, making it essential for ensuring compliance and avoiding enforcement actions.
Since 1990, the FAA has kept a public database of these crucial documents. These days, the agency is more selective, issuing interpretations only for questions that bring up new or legally significant issues. This makes every new interpretation that much more impactful.
Comparing FAA Guidance Documents
To really see why legal interpretations are in a class of their own, it helps to compare them to other documents the FAA puts out. Each one has a different job and a different level of authority.
Document Type | Purpose | Legal Binding Status |
|---|---|---|
Legal Interpretations | To clarify specific, ambiguous regulations in a binding manner. | Legally Binding. Represents the FAA's official enforcement position. |
Regulations (FARs) | To establish the official, mandatory rules of aviation. | Legally Binding. These are the actual laws all must follow. |
Advisory Circulars (ACs) | To provide guidance, best practices, and acceptable methods for compliance. | Not Legally Binding. Considered helpful but not mandatory. |
Getting this hierarchy right is key. An Advisory Circular might show you one way to comply with a rule, but a legal interpretation tells you what the FAA says the rule is.
For anyone operating in the National Airspace System, staying on top of these isn't just a good idea—it's a fundamental part of flying safely and legally. For an even deeper look, check out our pilot's guide to FAA legal interpretations.
How the FAA Creates Legal Interpretations
An FAA legal interpretation doesn't just materialize out of thin air. It’s the end result of a very deliberate, methodical process kicked off by genuine confusion out in the real world. The journey doesn't start inside an FAA office; it begins with a question from someone just like you.
The whole thing gets rolling when a person or company—maybe a pilot, a drone services business, or an aircraft maintenance shop—sends in a formal written request. They've hit a wall where the existing rules, the Federal Aviation Regulations (FARs), are either unclear or just don't seem to fit their specific situation. They need an official answer to make sure they're flying right.
These requests land on the desk of the FAA’s Office of the Chief Counsel (AGC), which is the agency’s in-house legal team. Here, specialized attorneys dig in to analyze the question and the regulations it touches on.
The Critical Review Process
Now, not every question that comes in gets a full-blown legal interpretation. The AGC attorneys are essentially gatekeepers, filtering the noise to focus on issues that are truly important. They’re specifically on the lookout for questions that are either “novel or legally significant.”
This is a critical standard. The FAA isn’t interested in wasting resources on questions that have already been answered or have a straightforward solution. Instead, they give their attention to issues that:
Involve new technology: How do rules written decades ago apply to modern drones or advanced aviation software?
Present a unique scenario: What happens when an operation doesn't fit neatly into any of the existing regulatory boxes?
Reveal widespread misunderstanding: If a lot of people are scratching their heads over the same rule, it’s a good sign that an official clarification is needed.
This selective approach is what makes each new FAA legal interpretation so valuable. It ensures the guidance they issue actually moves the needle and clarifies murky areas of aviation law for the entire industry.
The core purpose of the AGC's review is to provide clarity where it matters most. By focusing on novel issues, the FAA avoids repetitive guidance and instead directs its legal authority toward shaping the future of regulatory compliance.
From Request to Official Document
Once a request makes the cut, the real legal legwork begins. Attorneys take a deep dive into the specific FARs, looking at everything from legislative history and past interpretations to the ultimate goal of keeping our skies safe.
The infographic below shows the streamlined path from that initial question to an official FAA document.
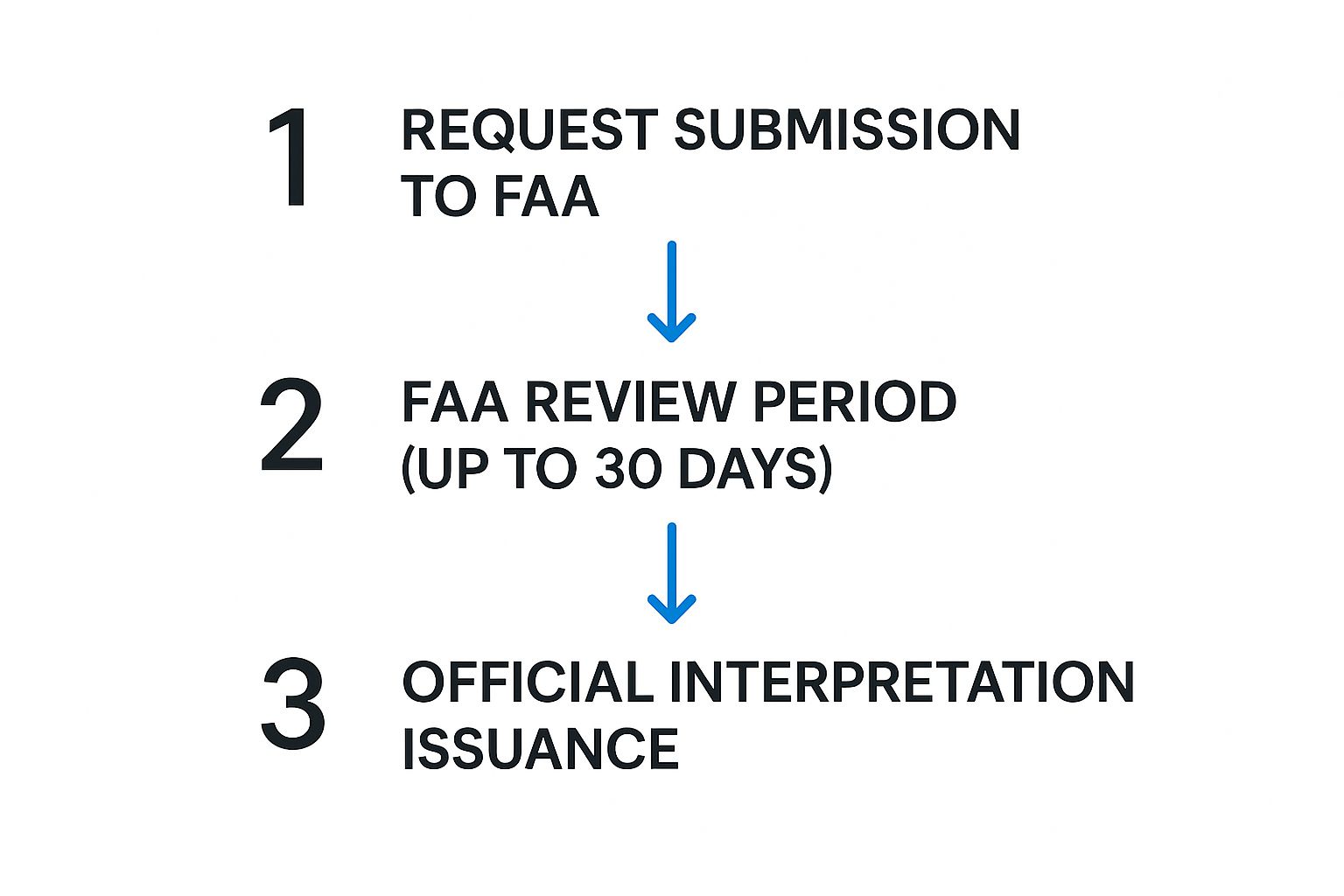
As you can see, it's a structured journey designed to make sure every interpretation gets a thorough and careful review before it becomes part of the official regulatory landscape. The final, crucial step is publishing the interpretation letter in the FAA's public database.
This is what gives the document its power. Posting it publicly transforms a private answer to one person's question into authoritative guidance that anyone in a similar spot can use to guide their own operations. This transparency is key to how FAA legal interpretations help create a consistent and predictable rulebook for everyone in aviation. By making these letters accessible, the agency gives the entire community the tools to understand and follow the rules of the sky.
The Balancing Act Behind FAA Decisions
When the FAA hands down a legal interpretation, it’s doing a lot more than just clarifying a rule. It’s walking a tightrope. On one side, its mission is to promote the aerospace industry. On the other, it has a non-negotiable duty to keep the public safe. These two goals don't always play nicely together.
This inherent tension means that FAA legal interpretations are never decided in a vacuum. Think of them as the product of a dynamic environment, constantly being pushed and pulled by industry pressure, new technology, public safety concerns, and even politics. It's a constant balancing act to keep the entire aviation system moving forward without a catastrophic fall.
This isn't just theory; it has real-world consequences. A single, high-profile incident can send shockwaves through the industry, forcing the agency to completely rethink its position on a rule and how it’s enforced.
The Ripple Effect of Safety Events
Nothing shifts the regulatory landscape faster than a major safety event. A tragic accident or a big maintenance scandal can trigger intense public outcry and congressional hearings, putting immense pressure on the FAA to take a more conservative, hardline approach.
We saw this play out in dramatic fashion after the 2008 Southwest Airlines inspection scandal. The incident put the FAA's dual role—promoter and regulator—under a microscope. Critics argued the agency's penalties weren't tough enough to be a real deterrent, which perfectly illustrates the difficulty of balancing industry health with strict enforcement. You can read more about the history and complexities of the FAA's dual mandate on Wikipedia.
It's a stark reminder of how external events can force the FAA’s hand. An interpretation that seemed perfectly reasonable one day can suddenly look dangerously lax the next.
How Industry Practice Shapes Interpretation
But the FAA doesn't just react to disasters. It also responds to the way the industry operates every single day. In some cases, a common industry practice that has been accepted for years can be suddenly upended by a new interpretation.
A perfect case study is the 2024 "Moss Interpretation," which dealt with the supervision of aircraft maintenance. For decades, the industry standard was that a certified mechanic could supervise a trainee "to the extent necessary." This was widely understood to allow for modern tools like video calls for remote oversight.
Then, a new interpretation dropped, suggesting the supervisor had to be "readily available, in person" at all times. This sent tremors through the entire maintenance community for a few key reasons:
It clashed with established workflows: The new take directly challenged decades of accepted practice.
It ignored modern technology: The ruling seemed to completely disregard the effectiveness of remote supervision tools.
It created huge operational hurdles: Requiring constant physical presence threatened to slow maintenance work and training programs to a crawl.
This case shows the incredible power of a single legal interpretation. A few sentences from the FAA's legal team can disrupt established business models and create massive operational headaches across the entire aviation sector.
The industry pushed back hard, and the FAA eventually issued a stay on the interpretation. This proves that the dialogue between regulators and the industry is a two-way street. It’s exactly why keeping a close watch on FAA legal interpretations is so vital. They aren't just static rules on a page; they are living documents that evolve with the changing realities of aviation.
How to Find and Use FAA Interpretations
Knowing that FAA legal interpretations exist is one thing. Knowing how to find them and use them for your own drone business is where the real power is. This is how you move from just knowing the rules to actively managing your compliance and risk—it's your playbook for getting official clarity, straight from the source.
So, where do you start? The FAA keeps an official online database called the Dynamic Regulatory System (DRS), which is the central library for every legal interpretation they’ve published. This is ground zero for your research.
Here is a look at the main search portal on the FAA's website.
The DRS lets you hunt for documents by keyword, regulation number, or date. This helps you cut through decades of guidance to find exactly what applies to your operation.
Effectively Searching the FAA Database
Just diving into the DRS and typing a broad term will probably give you hundreds of documents that are completely irrelevant. To find the specific FAA legal interpretations you need, you have to be a bit more strategic.
Think of yourself as a legal detective. You’re looking for a past "case"—an interpretation—that lines up with the facts of your own operational puzzle. Here are a few tips to sharpen your search:
Search by Regulation: If you have a question about a specific rule, like Part 107.31 (visual line of sight), just search for "107.31". This will show you every interpretation tied to that rule.
Use Precise Keywords: Instead of a simple phrase like "drone over people," try using the FAA's own terminology. Search for things like "operations over human beings" or "kinetic energy" to get much more accurate results.
Filter by Date: The FAA's position can change, and newer interpretations often replace older ones. Always filter for the most recent documents to make sure you’re working with the latest guidance.
Once you find a letter that fits your situation, it acts as a precedent. It gives you a legally sound foundation for your actions.
Applying an Interpretation to Your Operations
Finding a relevant interpretation is a huge win, but you have to apply it the right way. You should treat that document as official guidance for anyone in a situation that is substantially similar to what’s described.
If an interpretation says a specific type of drone flight is okay under certain conditions, you can feel confident moving forward with that same flight—as long as you meet those exact same conditions.
An existing FAA legal interpretation is your shield. It provides documented proof of the agency's position, which can be invaluable during an FAA ramp check or inquiry. It shows you've done your due diligence.
When to Request Your Own Interpretation
But what if you search and come up empty? This can happen. If you're dealing with a truly new situation—maybe involving brand-new tech or a unique business model—and there’s no existing guidance, it might be time to request your own interpretation.
To do this, you'll need to send a formal letter to the FAA's Office of the Chief Counsel. Your request has to be incredibly clear and detailed. Make sure you outline:
The Specific Facts: Clearly describe your proposed operation, the technology you're using, and the exact circumstances.
The Regulation in Question: Pinpoint the exact Federal Aviation Regulation (FAR) that you feel is unclear or ambiguous for your situation.
Your Specific Question: Ask a direct, pointed question about how that regulation applies to your specific set of facts.
How you frame your request is critical. The FAA gives priority to questions that are "novel or legally significant," so you need to show why your issue deserves a fresh look. Sometimes, major legislative changes can also create gray areas that need clarification. You can learn more about this by reading our insights on the FAA Reauthorization Act of 2024 and what it means for pilots.
Landmark Interpretations That Changed Aviation

Sometimes the best way to understand the real-world power of an FAA legal interpretation is to see it in action. These documents aren't just dry legal theory collecting dust on a shelf; they are genuinely impactful decisions that have directly shaped how pilots fly, mechanics wrench, and drone businesses operate today.
Let's dig into a few real-world examples that sent ripples through the entire aviation community.
Each case follows a familiar arc: a gray area in the regulations creates confusion or a problem, the FAA’s legal minds step in with a definitive clarification, and the industry has to adapt to the new normal. These are tangible moments where a single document from the Office of the Chief Counsel has redrawn the lines for day-to-day aviation practices.
For the drone community, this process has been front and center. Few topics have sparked more debate than the rules around complex operations, from how many drones one person can fly to the nitty-gritty of flying over people. In these areas, legal interpretations have been absolutely essential for setting the boundaries.
Key Drone Interpretations Under Part 107
When Part 107 first rolled out, it was a game-changer for commercial drone use. But the rules couldn't possibly cover every single scenario imaginable. This naturally led to pilots and companies asking critical questions that needed official answers.
One of the most significant early interpretations cemented the "one person, one drone" rule. It clarified, in no uncertain terms, that a single remote pilot in command cannot operate multiple small unmanned aircraft at the same time under standard Part 107 rules.
This decision didn't add a new regulation; it simply defined the edges of an existing one. But its impact was huge. It directly affected the scalability of certain drone delivery and survey operations, forcing companies to get creative by pursuing waivers or investing heavily in new automation technology to operate within that clear constraint.
Likewise, interpretations around flights over people and moving vehicles have been pivotal. Long before the official Operations Over People rule was finalized, FAA legal interpretations provided the first real guidance on how operators could use the waiver process to achieve an equivalent level of safety. They set precedents for what kinds of risk mitigation the FAA found acceptable, essentially paving the way for the formal regulation that followed.
To give you a clearer picture, here’s a quick breakdown of some of the most important interpretations for Part 107 pilots.
Key Interpretations for Part 107 Drone Operations
This table summarizes a few notable legal interpretations that have directly affected how commercial drone operators conduct their flights, and what it means for your daily missions.
Interpretation Topic | Summary of FAA's Position | Practical Impact for Operators |
|---|---|---|
Simultaneous Operations | One Remote Pilot in Command (RPIC) cannot operate more than one small unmanned aircraft at a time. | This prevents a single pilot from flying a "swarm" of drones without a waiver, requiring multiple pilots for certain large-scale missions. |
"Over" vs. "Above" | The FAA has clarified that flying "over" people generally refers to the area directly above them where an object could fall and cause injury. | This helped operators plan flight paths with more confidence, especially in urban areas, by defining exactly what to avoid to maintain compliance. |
Visual Line of Sight | The RPIC or a designated Visual Observer must be able to see the drone with their own eyes, without technological aids like FPV goggles or binoculars. | This ruling solidified the limits of standard operations and underscored why a specific waiver is absolutely necessary for Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) flights. |
These clarifications have been instrumental in building a foundation of safety and predictability for the entire commercial drone industry.
Major Rulings in Traditional Aviation
Of course, it’s not just the drone world that’s shaped by these rulings. Traditional aviation is just as reliant on these critical legal clarifications. Interpretations have settled long-standing debates over everything from pilot compensation to specific maintenance procedures.
A classic example is the "pro-rata share" rule found in 14 CFR § 61.113. This regulation lets private pilots share the direct costs of a flight with their passengers. But what exactly counts as a "pro-rata" share? And where is the line between sharing expenses and receiving "compensation"?
The answers have been defined through numerous FAA legal interpretations. These documents draw a firm line between legal, friendly expense-sharing and running an illegal charter operation. Without them, countless private pilots could easily find themselves in serious legal trouble without even realizing it.
Interpretations and Their Role in Aviation Safety
When you think about legal interpretations from the FAA, you might just picture a stuffy document clarifying some obscure rule for a pilot. But they’re so much more than that. These interpretations are actually a cornerstone of modern aviation safety. They provide the legal certainty that allows the entire industry to learn from itself, creating a culture built on trust and proactive problem-solving rather than fear of getting in trouble.
Think about it this way: how do you convince airlines and pilots to willingly hand over sensitive safety data—things like small mistakes they made or potential hazards they spotted? You have to give them a rock-solid guarantee that this information will be used to make things better, not to bring down the hammer of enforcement on them. This is where that legal framework becomes absolutely critical.
Protecting Critical Safety Data
A perfect real-world example of this system in action is the Aviation Safety Information Analysis and Sharing (ASIAS) program. Rolled out by the FAA back in 2007, this powerful system gathers and crunches massive amounts of voluntarily submitted safety data from all corners of the industry. The goal? To spot emerging risks before they have a chance to turn into accidents.
The whole thing works because of legal protections. It's the FAA legal interpretations of federal laws like 49 U.S. Code § 40123 that give these programs their strength. These laws ensure that any safety data shared voluntarily is kept confidential and shielded from public release or any kind of punitive action. This legal shield is what gives operators the confidence to share priceless safety insights without looking over their shoulder. You can actually read more about how these legal protections enable ASIAS data sharing directly from the Department of Transportation.
This spirit of collaboration is what allows the FAA and its industry partners to uncover subtle, system-wide safety trends that would otherwise fly completely under the radar. Without the solid legal footing that interpretations provide, this kind of proactive safety analysis just wouldn't be possible.
Fostering a Culture of Safety
At the end of the day, the link between legal clarity and real-world safety is all about building a just culture. When pilots and operators know the rules are clear and that reporting safety concerns in good faith is a protected act, they transform from passive rule-followers into active partners in the entire safety ecosystem.
By providing a legal framework for data protection, the FAA ensures that safety reporting is seen as a constructive act, not a liability. This shifts the focus from assigning blame to finding system-wide solutions.
This safety culture isn’t just for the big airlines; it extends to every part of aviation, including the booming drone industry. For commercial drone pilots, getting a handle on the legal landscape isn't just about staying compliant. It's about doing your part to contribute to a safer airspace for everyone.
Knowing the rules is the first step, and for most, that starts with understanding why you need a Part 107 license to fly for business. The clear standards set by FAA legal interpretations give pilots and companies the stability and confidence they need to invest in better training, safety systems, and voluntary reporting—making the skies safer for all of us.
Frequently Asked Questions About FAA Legal Interpretations
Working your way through aviation regulations can feel like a maze, but knowing how the system functions makes all the difference. To wrap things up, let's tackle some of the most common questions pilots and operators have about FAA legal interpretations.
How Long Does It Take to Get a Response?
There's no set timeline for getting a legal interpretation back from the FAA. The agency tends to prioritize requests it considers "novel or legally significant," which is their way of saying that questions about new tech or unresolved gray areas jump to the front of the line.
Because of this, don't be surprised if simple or previously answered questions don't get a response at all. For the more complex issues that the FAA does decide to review, you could be looking at a wait of several months—or in some cases, even longer.
Are Interpretations the Same as Laws?
No, an FAA legal interpretation isn’t a new law or regulation. In the real world, though, it carries a lot of legal weight. Think of it as the FAA's official, binding stance on what an existing rule actually means on the ground.
While not a regulation itself, an interpretation is given substantial deference by courts. This means it effectively represents the FAA's enforcement position, making it a critical document for anyone seeking to maintain compliance.
Can an Interpretation Be Changed?
Absolutely. An FAA legal interpretation isn't set in stone. While you could technically challenge one in court, judges usually defer to the agency’s expertise on its own regulations.
It's far more common for the FAA itself to update its position. An interpretation can be replaced or officially withdrawn if:
A new interpretation is issued with updated guidance.
The original regulation it was based on gets changed or replaced.
A major shift in technology or industry practices demands a fresh look.
Do I Need a Lawyer to Make a Request?
While the FAA doesn't require you to hire a lawyer to submit a request, it's a very good idea. Bringing in an aviation attorney can seriously boost the odds of your request getting the attention it deserves.
A good lawyer knows how to frame the question perfectly, making sure all the necessary facts are included and the legal issue is spelled out with clarity. That professional polish helps your request stand out and shows the FAA's legal team that it’s a significant issue worth their time.
Properly registering your aircraft is another foundational step for compliance. For more information, our complete guide on FAA drone registration can walk you through the process stress-free.
At JAB Drone, we're committed to providing the expert insights you need to fly safely and confidently. Explore our in-depth reviews and guides to stay ahead in the dynamic world of drone technology at https://www.jabdrone.com.




Comments